G r e e n f a s e r Products for Organic farming
Applications
Photos
Broschure
Yellow Line (pdf)
Yellow Line
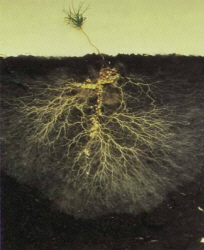
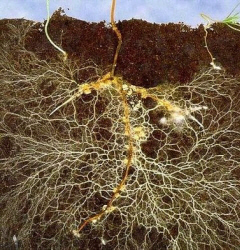
Effects on radical apparatus
Example of development and the protection roots

Auxiliary products for the accelerated development and biological growth
of plants and for soil
improvement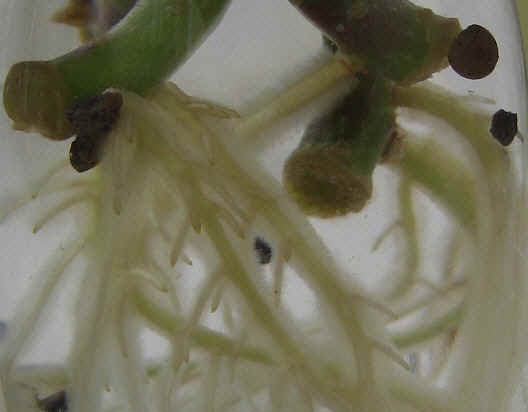
What is mycorrhiza
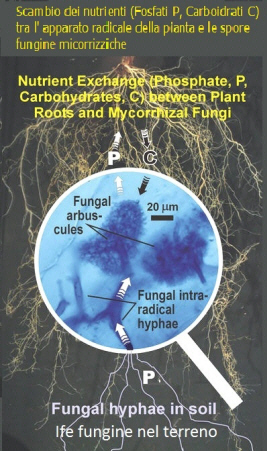
Mycorrhiza, in agriculture and horticulture, is a cultivation technique that consists in attacking the roots of the plant fungal pathogens that do not create it with a state of symbiosis with the mutual exchange of nutrient intake.
The fungal spore gets
carbs (produced during photosynthesis) from the vegetable plantís roots
and from the plant itself, while the plant receive water, mineral and
nutrient substances from the fungal spore; these nutrient advance a
natural development and a faster growth of the plant.
The symbiotic association composed of a fungus and a plant is called
mycorrhizza; this technique is also experimented as treatment for
bio-redevelopment of the soil.
The fungus draws by the roots of the plant nutrients, while the plant receives water and minerals from the fungus that will encourage the development and growing more rapidly.
Mycorrhizas form a mutualistic relationship with the roots of most plant species.
They are typically found in the rhizosphere of a root system.
This mutualistic association provides the fungus with relatively constant and direct access to carbohydrates, such as glucose and sucrose supplied by the plant. The carbohydrates are translocated from their source (usually leaves) to root tissue and on to fungal partners.
In return, the plant gains the benefits of the mycelium's higher absorptive capacity for water and mineral nutrients (due to comparatively large surface area of mycelium:root ratio), thus improving the plant's mineral absorption capabilities.
Mycorrhizal plants are often more resistant to diseases, such as those caused by microbial soil-borne pathogens, and are also more resistant to the effects of drought.
Importance and advantages of mychorrhizzal spores
The importance of mychorrhizal spores is not limited to assimilation of water and nutrients from the ground.
Plants associated with mychorrihizal fungi seem to be more competitive and more resistant towards environmental tensions.
|
∑ Acquisition of nutrients usually not available to plants (ex: N in organic compounds) |
∑ Ability to remove phenolic compounds and toxic metals from the ground (mercury, lead, zinc etc.) |
|
∑ Defence from hydro-stress |
∑ Defence from Nematodes and parasitic fungi |
|
∑ Nutrients accumulation |
∑ Establishment of nutritional nets |
|
∑ Fungus ifas support seeds generation in ground |
∑ Transfer of nutrients from dead plants to alive plants |
How does the Mychorizza spore act on the plant?
The Mychorizza spore starts the symbiotic relationship with the plant, growing with it, covering itís roots and extracting all nutrients from the soil to feed the plant.
The same happens with water and the plants receives just the needed water amount: the mychorizza spore acts as storage device, supplier and filter at the same time (useful during droughts) and receives in return carbohydrates, which the plants produces during photosynthesis. At this point the plant grows biologically in the ground, with an important development in roots volume (usually they double their size).
Obviously also the external part of the plant reacts in the same way with a consequent increase in weight and dimension of the fruit (up to 50%).
Therefore Mychorizzation increase plants endurance against droughts, pathogens, disease and parasites (roundworms and larvae).
Shortly
How do products work ? Which are the influent factors ?
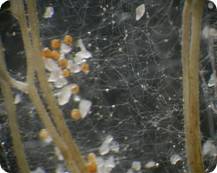
Spores effect directly on the plant roots; they assume complete control by creating a reticular structure (in picture) which envelop the roots isolating them from the soil and/or from the surrounding substratum.
Therefore they provide for:
∑ The passage of nutritious substances, extracted from the soil
∑ The passage of water as they work as accumulators, allowing the plant to get the amount of water needed.
∑ The increasing in the roots dimension.
However this is not enough if the soil is poor in nutrients.
Bacteria fulfil this task by providing spores essential and necessary nutrients, included atmospheric nitrogen.
The specific fertilizer creates for the plant the ideal, balanced eco-system, necessary for his best development and growth by stabilising the optimal soil ph.
How often should products be used?
Usually this spores treatment should be used only one time since if the symbiosis has already taken place there is no need of another treatment.
Treatments with soil bacteria only and special fertilizer must be repeated during the year, with regard to the plant and soil quality
In horticulture treatments must be repeated during sowing time.
For any special needs and further information please consult us !
Our products are not genetically modified (GMO) and is not used any genetic modification process for the preparation of its components
Respect the Environment and keep it clean!
Nature will be grateful!